
According to figures released by Energy Victoria, Victorians spend a third of their energy bill on heating, so depending on your property space, ducted heating and ducted electric heating and cooling can be well and truly worth the upgrade.
Whether you’re planning to renovate an existing home or you’re investing in a new build, it’s always a good idea to weigh whether gas or electric heating is for you. Electric heating systems are usually a clear winner, but you may prefer a gas system if you have a smaller space.
This article is an excellent guide to understanding each heating mode, their energy consumption, energy costs for both small and large spaces, their greenhouse gas emissions over time, and how to choose for your lifestyle.
What is gas ducted heating, and what is ducted electric heating and cooling? Here is a quick explanation of both and the reasons you may or may not use them to regulate the temperature of your space.
Drawing air from inside the home, this is then heated in a gas furnace and blown through ducts to outlets in different areas of your home. A thermostat is near the return air grille and controls the inside temperature. With this in mind, what are the main advantages of gas-ducted heating?
Reasons to use it? It heats all rooms–or designated rooms from zoning–very quickly. Only heating areas you use to reduce the gas you’re using overall, and in some cases, different rooms can be controlled with thermostats.
Reasons not to use it? Air circulation fans use excessive electricity, especially since gas ducted heating runs on natural gas. It is also significantly more expensive to operate than electric reverse cycle systems, and a separate cooling system is needed during warmer days.
Offering whole-house heating and cooling through one set of ducts instead of just heating alone, electric ducted heating and cooling is located in the roof space.
Like gas ducted heating, heat from outside is pulled into the central unit and blown through duct outlets in the home. Air is returned to the indoor unit to be reheated, and a thermostat controls the indoor temperature. The system doesn’t generate heat directly using an electric heating element; it uses heat pump technology to extract heat from outside air. Arguably, this is the most efficient form of electric heating!
Why should you use it? A single unit provides enough heating and cooling for your home, so you don’t need to invest in a separate air conditioner. Most systems also allow the home to be split into zones.Why wouldn’t you use it? The system’s outdoor compressor can be noisy and conflict with neighbours’ or council regulations. You may also need three-phase power for larger systems, which can have a high energy consumption. In some cases, this can increase the electricity cost.
Need advice on your heat exchanger, or do you want to make the switch from ducted heaters to ducted electric? With reverse-cycle heating and cooling to homes in Templestowe, Warranwood, Camberwell, Ringwood, you can trust Australian Climate Systems to provide top-quality products, installation, and service for your heating and cooling can give you an upfront cost estimate and a guide to popular options.
The energy-efficiency rating is very important, but what is the difference between gas-ducted heating and ducted electric heating and cooling?
Gas-ducted heating has gas energy labels that allow you to compare different heating options. The higher the rating, the more efficient it is for your home. Gas heating in homes isn’t the best recommendation in 2024, but if you’re considering it, be certain of its energy rating.
If you plan to build your home, ask about the star rating. It is worth paying more for five-star ratings or higher as your family will save more in the long term. A system with zoning capacity will support these costs. Gas ducted systems can also lose energy through their ductwork, so ask your installer about the home’s R-level or insulation level. Always aim for an R-value of 1.0 or higher.
The best temperature to set your heating is 18 to 20 degrees; every 1-degree increase can add 10% to your heating bill. Clean the air filter monthly during winter so it operates effectively, and service the gas furnace at least every two years.
Since April 2020, new ducted reverse cycle air conditioners with a cooling capacity of less than 30kW have required a Zoned Energy Rating, ideally a high rating, making the system efficient for your home.
Ducted systems need a Zoned Energy Rating but are not required to display it when sold. If you are in doubt, always ask a heating and cooling professional about the rating and if it is best for your lifestyle.
If you’re buying a new system, you can choose between two types of compressors. A standard compressor will switch on and off depending on thermostat control, and a variable-speed compressor, known as an inverter, is quieter, more efficient, and runs at a lower speed as soon as your room has reached the desired temperature.
Zone your system is great for limiting heat to areas you’re using, and this depends on the design of your home and the placement of the return air grille. The stronger your zoning, the more control you will have over your energy usage.In some cases, there can be energy losses due to ductwork when the air conditioner is operating. The more solid the insulation, the lower your heat losses will be. Clean the return air grille filter every month, and service the system regularly per manufacturer instructions. If you’d like to learn more, check out this article on reverse cycle vs gas ducted heating and how it can benefit you throughout all seasons.
The installation cost of your heating and cooling system depends on the number of outlets you need, the size of the system, the brand you choose to install, and other factors for your home.
Gas ducted heating is generally less expensive to install, with an average cost of $3000 to $7000.
Reverse cycle ducted electric heating and cooling averages around $6000 to $12,000.
If you’re looking for adequate electric heating options or ducted heating systems, Australian Climate Systems provides efficient reverse-cycle heating and cooling to Mont Albert, Kew, Croydon, Caulfield, and surrounding areas.
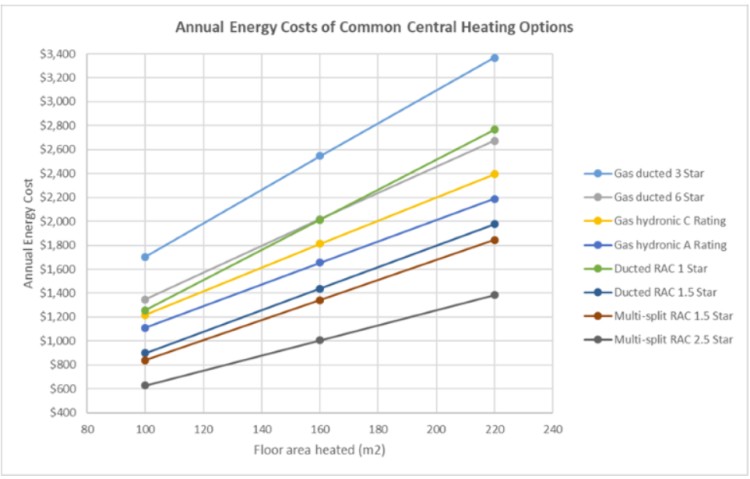
Image Source: Sustainability Victoria
Running costs for gas-ducted heating and ducted electric heating and cooling are some of the most important factors when installing one in your home.
Reflecting the gas price increase from 1 February 2023 and the electricity price rise from July 2023, here is an extensive update on what you can expect. What are the average running costs for both systems, and how will you decide?
For unzoned gas ducted heating, a 3-star energy rating has an annual energy cost of $1,704—a 4-star costs $1,528, and a 6-star costs $1,347 for the year.
On the other hand, the ducted reverse cycle air-conditioner (unzoned) is $1,258 annually when using a 1-star system and $899 for the year with a 2-star system.
Ducted gas heating systems (unzoned) systems with a 3-star energy rating cost $3,368 annually, 4-star systems cost $3,025, and 6-star systems cost $2,674 annually.
A 1-star ducted reverse cycle air conditioner (unzoned) will cost $2768 for the year, and a 2-star costs $1,977 annually.
Natural gas heating with a 3-star rating averages $223 annually, whereas a 4.5 star costs $213 annually. A gas heater (LPG) with a 3-star energy rating costs $324; a 4.5 star adds up to $289 for the year.
A ducted heating unit (natural gas) with a 3-star energy rating averages $1024 annually, with a 4.5 star averaging $911 annually. Gas heating (LPG) with a 3-star rating is around $1,621, whereas a 4.5-star costs around $1,443 annually.Reverse cycle air-conditioning with a 1.5 energy rating will cost $626 annually, and 2.5 stars add up to around $469 annually.
You need to understand your system’s listed energy usage, such as MJ/h for gas and kW for electricity, and your tariff rate, which is commonly listed on your electricity bill.
Calculate hourly costs for gas ducted heating by multiplying the tariff rate by megajoules per hour for an hourly running cost.
Calculate hourly costs for ducted electric reverse cycle heating and cooling by multiplying the tariff rate by the kilowatts for an hourly running cost.
To estimate running costs for a colder climate such as Ballarat and whether it is energy-efficient, multiply these figures by 1.5. For a warmer climate such as Mildura, multiply these figures by 0.8. As for a 5-star home in Melbourne’s climate, multiply the costs by 0.4. 6-star homes should multiply these costs by 0.3.
Keep in mind that this is a guide only, with figures last updated in June 2023. Accurate costs will depend on how insulated your house is, the heated area, your thermostat settings, local climate, energy tariffs, and how insulated your home is.
When installing a heating or cooling indoor or outdoor unit, it’s important to consider its environmental impact. With gas-ducted heating and ducted electricity, what is their carbon footprint?
A ducted reverse cycle air-conditioner (unzoned) with a 1-star energy rating produces 18.6 tonnes of greenhouse gas emissions over ten years, whereas a 2 star produces 13.3 GHG emissions.
Gas ducted (unzoned) with a 3-star energy rating uses 29.7 GHG emissions over ten years, a 4-star uses 26.6, and a 6-star uses 23.4 GHG.
An unzoned ducted reverse-cycle air conditioner with a 1-star energy rating produces an average of 41.0 greenhouse gas emissions every ten years, while a 2-star system produces around 29.3 tonnes.
For unzoned gas-ducted heating, a 3-star system produces 65.4 GHG emissions each decade, a 4-star system produces 58.6, and a 6-star rating produces 51.5 tonnes of GHG.
As masters of heating solutions and cooling solutions, Australian Climate Systems offers sales and installation, warranty and repairs, and service, repair or maintenance when you need that yearly inspection. With 25 years in business, our team provide generous workmanship guarantees, offers brands from Bonaire to Brivis and Daikin, and supplies only the best for your home.
Whether you are looking to navigate ducted electric systems instead of electric heaters, want add-on cooling to suit you all year round, or think a new system will complement your solar panel, our team is your best supplier, installer, and professional.
Contact us today at 03 9762 4444 or visit us in Chirnside Park, Victoria, to get a satisfying new system.